Last Updated: November 30, 2025
1. Key Takeaways
A neural network is a layered mathematical model that learns patterns from data.
It consists of neurons (nodes) connected by weights that adjust during training.
Neural networks power deep learning and form the foundation of LLMs, computer vision, speech systems, and more.
They learn hierarchical representations: simple → complex features.
Modern AI breakthroughs are all built on neural networks, especially transformers.
Table of Contents
2. What Is a Neural Network?
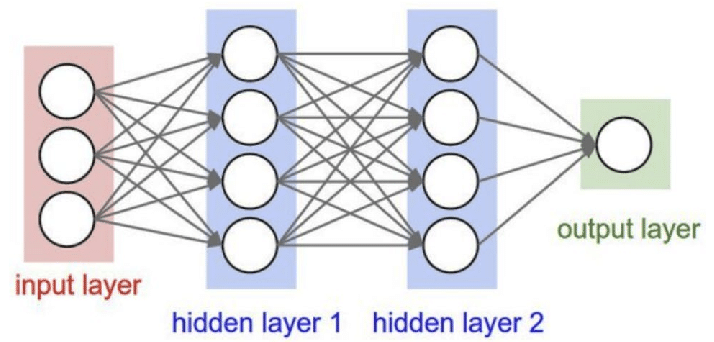
Basic Neural Network Diagram
A neural network is a computational system composed of interconnected neurons (nodes) arranged in layers. These layers transform raw input data into meaningful predictions, enabling the model to learn patterns automatically.
Neural networks power:
GPT, Claude, Gemini, Llama
image models like Stable Diffusion
speech recognition
recommendation algorithms
fraud detection
robotics
self-driving car perception
They are the foundation of deep learning.
3. How Neural Networks Work
Neural networks operate by passing data through multiple layers that each perform small mathematical transformations.
Input Layer — receives raw data
Hidden Layers — extract patterns step-by-step
Output Layer — generates predictions
Weights and biases determine how strongly neurons influence one another.
Activation functions introduce non-linear behavior, allowing the network to learn complex patterns.
This is how networks learn to detect text meaning, image features, audio signals, and more.
4. Types of Neural Networks
Neural networks come in various architectures designed for different data types.
Feedforward Neural Networks (FNNs)
Basic layered networks used for simple predictions.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
Handle images, videos, and spatial patterns.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
For sequence data (older NLP before transformers).
Transformers
The architecture behind all modern LLMs and many multimodal models.
Autoencoders
Used for compression, anomaly detection, and representation learning.
GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks)
Two-network systems for generating synthetic images, deepfakes, and creative outputs.
5. Neural Networks vs Deep Learning vs Machine Learning
Neural networks are often confused with deep learning or machine learning. Here’s how they relate:
Machine Learning → Deep Learning → Neural Networks → Transformers → LLMs
TABLE 1 — The AI Hierarchy
Level | Meaning | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Machine Learning | Algorithms that learn from data | Random Forest, XGBoost |
Deep Learning | ML using multi-layer neural networks | CNNs, RNNs, Transformers |
Neural Networks | Core architecture for deep learning | FNNs, RNNs |
Transformers | Modern neural network | GPT, Gemini |
LLMs | Large transformer models | GPT-4.1, Llama 4 |
6. Components of a Neural Network
Neurons — perform computations
Weights & Biases — learnable parameters
Layers — input, hidden, output
Activation Functions — ReLU, Sigmoid, GELU
Loss Function — measures prediction error
Optimizer — updates weights (Adam, SGD)
Together, these components enable neural networks to learn patterns autonomously.
7. How Neural Networks Learn (Training Process)
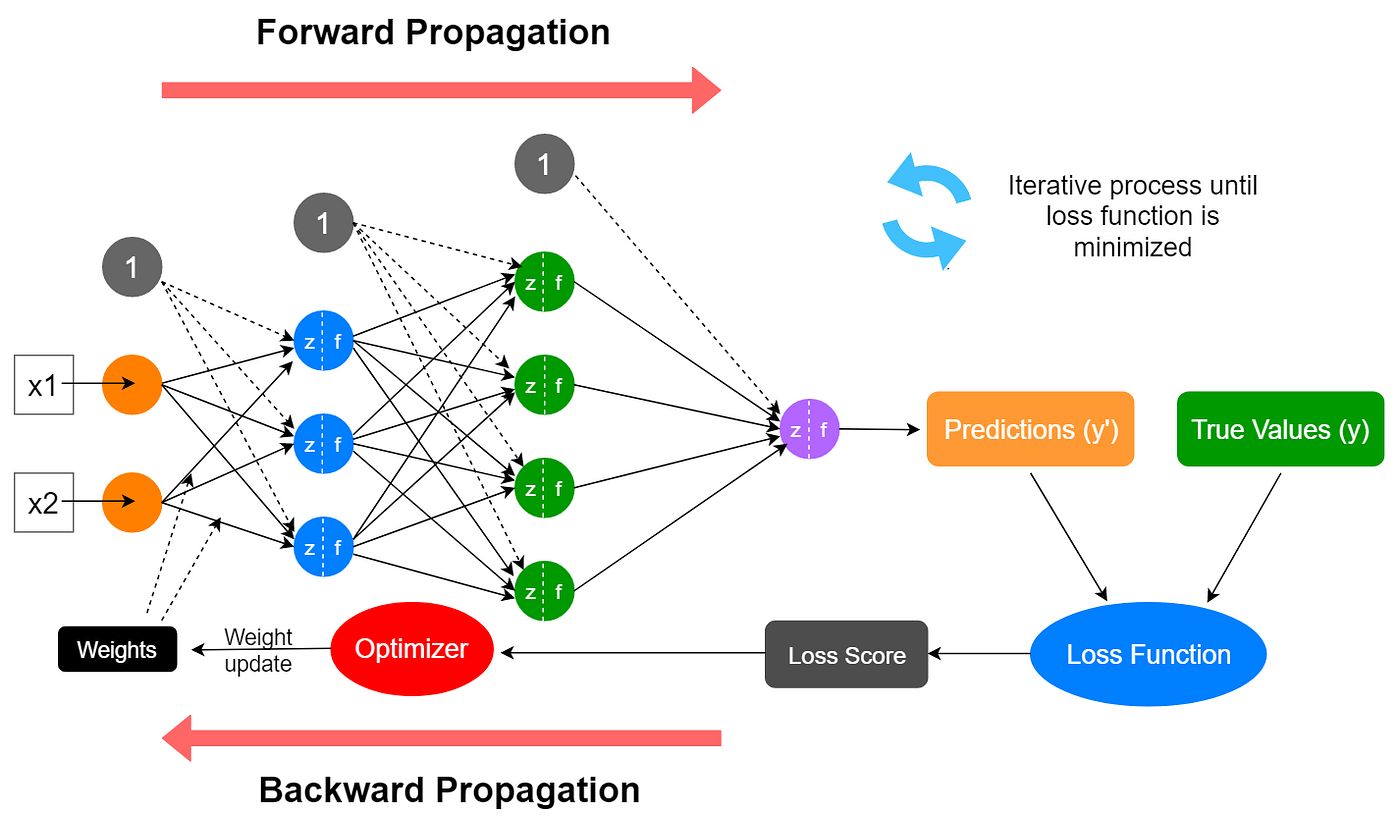
Neural Network Training Process
Neural networks learn through repeated prediction-and-correction cycles.
Forward Pass — model predicts
Loss Calculation — measures error
Backpropagation — computes gradients
Optimization — updates weights
Epochs — repeats many times
TABLE 2 — Neural Network Training Workflow
Phase | What Happens | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
Forward Pass | Model predicts | Finds patterns |
Compute Loss | Measures error | Guides learning |
Backpropagation | Computes gradients | Adjusts weights |
Optimization | Updates parameters | Reduces error |
Epochs | Many cycles | Improves accuracy |
8. Real-World Applications
Neural networks power major AI advances across industries.
Computer Vision
Object detection, autonomous driving, medical imaging.
NLP
LLMs, translation, summarization, chatbots.
Speech & Audio
Voice assistants, real-time transcription, speaker recognition.
Finance
Fraud detection, risk scoring, algorithmic trading.
Healthcare
Diagnostics, drug discovery, patient risk prediction.
Neural networks enable machines to understand text, vision, audio, and structured data at a level previously impossible.
9. Limitations and Challenges
Neural networks have significant constraints.
Data Requirements — large, high-quality datasets
Compute Costs — expensive GPU/TPU needs
Black-Box Behavior — limited interpretability
Bias & Fairness Issues — reflects training data
Overfitting Risks — memorization instead of generalization
Energy Consumption — large environmental footprint
These challenges continue to drive innovation in more efficient and transparent AI systems.
10. The Future of Neural Networks
Key advancements shaping the future:
State-Space Models (SSMs)
Faster sequence processing than transformers.
Mixture-of-Experts (MoE)
Specialized sub-networks reduce inference cost.
Multimodal Neural Networks
Models that understand text, images, audio, and video together.
Tiny Efficient Models
Small, specialized networks for industry-specific tasks.
Neural-Symbolic Systems
Combining neural networks with symbolic reasoning for better interpretability.
Neural networks will remain the core of next-generation AI models.
Glossary
Neuron — computational unit
Weight — connection strength
Backpropagation — training algorithm
Activation Function — creates non-linear learning
Epoch — one full pass through training data
Transformer — modern neural network architecture
FAQ
Are neural networks and deep learning the same?
Deep learning uses neural networks, but neural networks are the building blocks.
Is a transformer a neural network?
Yes — a highly specialized one.
Do neural networks require large datasets?
Most high-performance models do.
Are all AI models neural network–based now?
Nearly all modern AI systems rely on neural networks.
Subscribe to AI Business Weekly
Daily AI news, explained simply.




