Last Updated: November 30, 2025

Computer vision system
1. Key Takeaways
Computer vision enables machines to interpret and analyze images and videos.
It uses deep learning models like CNNs, Vision Transformers, and diffusion models.
Applications span self-driving cars, surveillance, medical imaging, robotics, and e-commerce.
Computer vision extracts meaning from pixels: objects, faces, actions, depth, and patterns.
It is one of the biggest fields inside AI and continues accelerating rapidly.
Table of Contents
2. What Is Computer Vision?
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence focused on enabling computers to understand images and videos.
It gives machines the ability to:
detect objects
recognize faces
interpret scenes
understand motion
identify medical abnormalities
navigate environments
Computer vision is essential to:
autonomous driving
drones
robotics
medical diagnostics
manufacturing automation
retail analytics
smartphone cameras
In simple terms:
Computer vision teaches machines how to “see.”
3. How Computer Vision Works
Computer vision systems follow a multi-step process:
Image Input
Raw pixels enter the model.
Feature Extraction
Deep learning models identify edges, shapes, textures, and regions.
Object Understanding
Models classify, detect, segment, or track items.
Decision / Output
The system outputs:
bounding boxes
segmentation masks
labels
actions
movement predictions
Computer vision relies heavily on neural networks — especially convolution, attention, and transformer-based designs.
4. Core Computer Vision Tasks
Here are the major tasks computer vision models solve:
Image Classification
Assigning a label to an entire image (e.g., “cat”).
Object Detection
Finding multiple objects using bounding boxes.
Image Segmentation
Pixel-level understanding (semantic or instance segmentation).
Facial Recognition
Identifying people in images.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
Extracting text from images.
Pose Estimation
Understanding body or hand positions.
Depth Estimation
Inferring distance from a single image.
Tracking
Following objects across frames.
These form the backbone of modern vision systems.
5. Popular Computer Vision Models
📊 TABLE 1 — Major Computer Vision Model Types
Model Type | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
CNNs | Feature extraction | ResNet, VGG, MobileNet |
Vision Transformers | Attention-based vision | ViT, DeiT |
Hybrid Models | CNN + attention | ConvNeXt |
Object Detection Models | Bounding boxes | YOLO, Faster R-CNN |
Segmentation Models | Pixel-level maps | U-Net, Mask R-CNN |
Diffusion Models | Image generation | Stable Diffusion, DALL·E 3 |
6. Components of a Computer Vision System
Convolution Layers
Extract spatial patterns.
Pooling Layers
Reduce dimensionality.
Transformers
Capture global relationships across an image.
Training Datasets
ImageNet, COCO, OpenImages, medical datasets.
Annotation Labels
Boxes, masks, classes, landmarks.
Loss Functions
Classification loss, bounding box loss, segmentation loss.
Computer vision requires large-scale, carefully labeled datasets.
7. How Computer Vision Models Are Trained
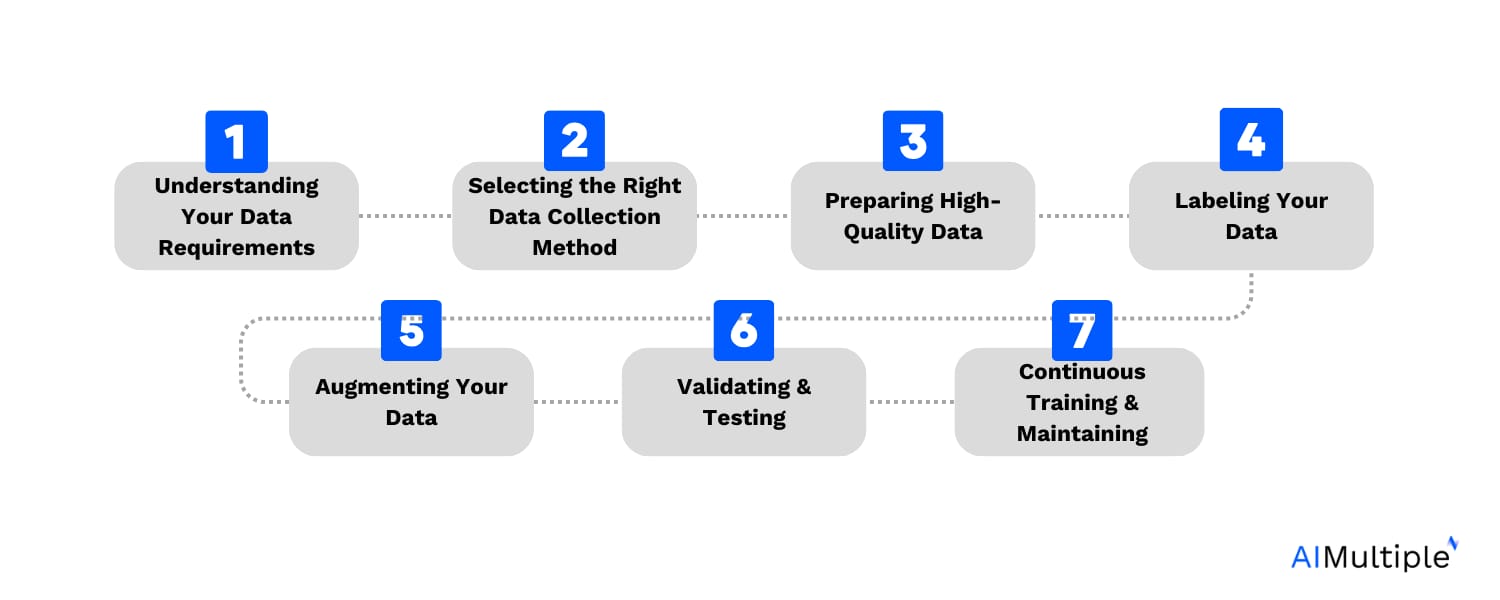
Computer Vision Training Workflow
Computer vision training includes:
1. Forward Pass
Model analyzes images.
2. Loss Calculation
Compares predictions to ground truth.
3. Backpropagation
Adjusts weights to improve accuracy.
4. Augmentation
Flips, crops, rotates, and modifies images to improve generalization.
5. Evaluation
Checks accuracy, IoU, F1 scores, and precision.
📊 TABLE 2 — Vision Training Pipeline
Step | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Input Augmentation | Modified images | Avoid overfitting |
Forward Pass | Model interprets image | Extract patterns |
Loss Calculation | Compare to labels | Measure correctness |
Backpropagation | Gradient updates | Reduce error |
Validation | Test performance | Ensure generalization |
8. Real-World Applications
Autonomous Driving
Lane detection, pedestrian detection, hazard prediction, depth estimation.
Healthcare
Tumor detection, X-ray reading, MRI analysis.
Retail & E-Commerce
Product classification, visual search, checkout automation.
Manufacturing
Defect detection, quality control.
Security & Surveillance
Face recognition, movement tracking.
Robotics
Navigation, object manipulation, environment understanding.
Computer vision is one of the most commercially important branches of AI.
9. Challenges and Limitations
Computer vision faces several constraints:
Environment Sensitivity
Lighting, angles, weather affect accuracy.
Data Requirements
Needs large, diverse datasets.
Bias
Training data inconsistencies can lead to unfair predictions.
Computational Costs
High GPU/TPU requirements.
Privacy Concerns
Especially with facial recognition.
Generalization Issues
Models may fail on unfamiliar environments.
10. The Future of Computer Vision
Upcoming innovations include:
Multimodal Vision-Language Models
Models like GPT-4.1, Gemini, and Claude that combine text + images.
3D Vision
Depth-aware perception for robotics and AR.
Edge Vision Models
Small, fast models for phones, drones, and IoT devices.
Self-Supervised Learning
Learning from unlabeled images at massive scale.
Generative Vision Models
High-fidelity image, video, and world simulation.
Vision Agents
AI systems that see, reason, and act.
Computer vision is evolving from simple labeling to full scene understanding and world modeling.
Glossary
CNN — Convolutional Neural Network.
OCR — Optical Character Recognition.
Segmentation — Pixel-level classification.
IoU — Intersection over Union metric for detection.
Backpropagation — Training algorithm.
Transformer — Attention-based neural network.
FAQ
Is computer vision the same as image processing?
No — computer vision uses AI; image processing uses mathematical filters.
Do all computer vision models use deep learning?
Modern ones do — CNNs and transformers dominate.
Is computer vision part of AI?
Yes — it’s a major subfield.
Is computer vision used in smartphones?
Everywhere — cameras, filters, face unlock.
Subscribe to AI Business Weekly
Daily AI news, explained simply.




