Last Updated: November 30, 2025
Machine Learning Concept Diagram
1. Key Takeaways
Machine Learning (ML) is a branch of AI that enables computers to learn patterns from data rather than being explicitly programmed.
ML powers everything from recommendation systems to fraud detection to language models.
There are three main types of ML: supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning.
ML models improve through training, evaluation, and optimization.
ML is the foundation for modern AI systems, including deep learning and large language models.
Table of Contents
2. What Is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning (ML) is a method of teaching computers to learn directly from data. Instead of writing rules manually, developers feed large datasets into algorithms, and the system automatically learns patterns, relationships, and behaviors.
ML models can:
classify text and images
predict future outcomes
detect anomalies
identify patterns
generate new content
personalize recommendations
make decisions based on learned data
Machine learning is the foundation of today’s AI revolution. Large Language Models (LLMs), such as GPT-4 and Claude, are built on top of deep learning—a specialized form of ML.
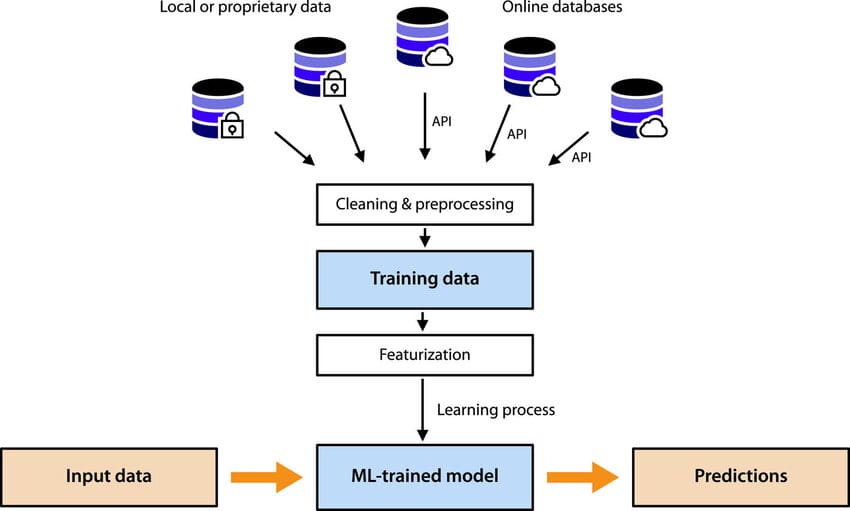
3. How Machine Learning Works
Machine learning follows a simple but powerful process:
1. Data Collection
Gather examples, such as text, images, or numerical data.
2. Data Preparation
Clean, label, and structure data for training.
3. Model Selection
Choose suitable algorithms (e.g., neural network, decision tree, SVM).
4. Training
Feed data into the model to help it learn patterns.
5. Evaluation
Test the model’s accuracy on unseen data.
6. Optimization
Tune parameters to improve performance.
7. Deployment
Use the model in real-world applications.
This cycle repeats as models improve over time.
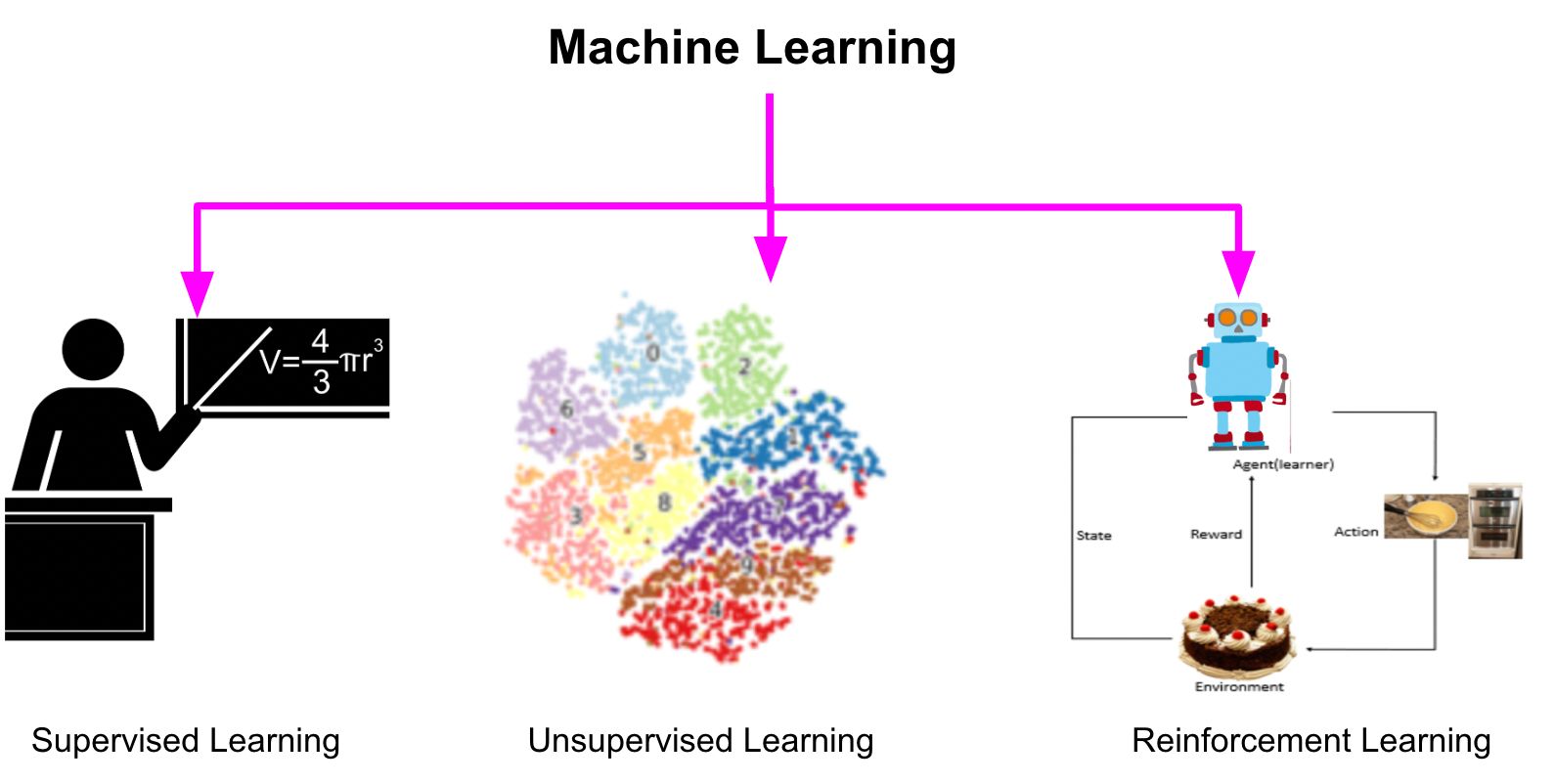
4. Types of Machine Learning
Machine learning is typically divided into three key categories.
📊 TABLE 1 — Types of Machine Learning
ML Type | Description | Best For | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
Supervised Learning | Model learns from labeled data (input → correct output). | Classification, prediction. | Fraud detection, spam filtering. |
Unsupervised Learning | Model finds patterns in unlabeled data. | Clustering, anomaly detection. | Customer segmentation, topic modeling. |
Reinforcement Learning | Model learns by trial and reward. | Decision-making, optimization. | Robotics, game agents, autonomous systems. |
Each type of ML supports different real-world use cases and industries.
5. Popular Machine Learning Algorithms
Different ML techniques solve different problems. Here are some of the most widely used algorithms:
Linear Regression
Predicts numerical outcomes using straight-line relationships.
Logistic Regression
Used for binary classification (e.g., spam vs. non-spam).
Decision Trees
Model decisions based on branching paths.
Random Forests
Ensemble of many decision trees for higher accuracy.
Support Vector Machines (SVMs)
Finds boundaries between classes.
K-Means Clustering
Groups items into clusters without labels.
Neural Networks
Multiple layers for complex learning — the basis of deep learning.
These form the “toolbox” used by ML engineers, depending on the problem and data available.
Types of Machine Learning Diagram
6. Training, Validation, and Testing
Machine learning models require structured datasets split into different groups.
📊 TABLE 2 — ML Dataset Splits
Dataset Split | Purpose | Percentage (Typical) |
|---|---|---|
Training Set | Teaches the model using labeled data. | 70–80% |
Validation Set | Tunes parameters and prevents overfitting. | 10–15% |
Test Set | Measures final performance on unseen data. | 10–15% |
These splits ensure that models generalize well and don’t simply memorize data.
7. Real-World Applications of Machine Learning
Machine learning powers entire industries today.
Healthcare
Disease prediction, medical imaging, patient risk analysis.
Finance
Fraud detection, credit scoring, algorithmic trading.
Retail & E-commerce
Recommendation systems, price optimization, inventory forecasting.
Marketing
Segmentation, personalization, lead scoring.
Transportation
Route optimization, autonomous vehicles.
Manufacturing
Predictive maintenance, quality assurance.
Content & Media
Spam detection, content moderation, recommendation engines.
AI Agents & LLMs
Machine learning is the foundation for transformers and large language models.
ML has become a universal technology — from startups to global enterprises.
8. Supervised Learning Explained
Supervised learning is the most common form of ML. It uses labeled data, where each example includes the correct answer.
Examples:
Email → “spam” or “not spam”
Image → “cat” or “dog”
Transaction → “fraud” or “legitimate”
The model learns patterns linking inputs to outputs.
Popular supervised algorithms:
Linear regression
Decision trees
Random forests
XGBoost
Neural networks
Supervised learning drives the majority of enterprise ML use cases.
9. Unsupervised Learning Explained
Unsupervised learning finds patterns in datasets without labels.
Examples:
Segmenting customers into groups
Identifying trending topics in text
Detecting unusual behavior in network logs
The goal is discovery, not prediction.
Popular unsupervised algorithms:
K-means clustering
PCA (dimensionality reduction)
Autoencoders
Hierarchical clustering
Businesses use unsupervised learning to uncover hidden insights.
10. Reinforcement Learning Explained
Reinforcement learning (RL) teaches an agent to make decisions through rewards and penalties.
Examples:
Robots navigating environments
Self-driving cars
AI game players (AlphaGo, AlphaZero)
Dynamic pricing systems
The agent takes actions, receives rewards, and learns the best strategy.
Deep reinforcement learning combines RL with neural networks, enabling complex behaviors.
11. Deep Learning: A Subset of ML
Deep learning uses large neural networks with many layers. It is responsible for:
image recognition
speech transcription
LLMs like GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini
video analysis
autonomous systems
Deep learning solved problems traditional ML could not, making it one of the defining breakthroughs of the last decade.
12. Advantages and Limitations of Machine Learning
Advantages
Learns patterns automatically
Scales to large datasets
Improves over time
Handles complex problems
Powers modern AI systems
Limitations
Requires large amounts of data
Computationally expensive
Can inherit bias from datasets
Lacks human-like understanding
Can generate incorrect predictions
Understanding these strengths and weaknesses is key to successful deployment.
13. The Future of Machine Learning
Machine learning continues to evolve rapidly.
Trends to watch:
Lightweight models for edge devices
AI agents that learn autonomously
Multimodal systems (text + vision + audio)
More efficient architectures (SSMs, MoE)
Enterprise-grade ML observability and governance
Privacy-preserving ML (federated learning)
ML will remain the foundation of AI for the next decade.
14. Glossary
Machine Learning: Algorithms that learn from data.
Model: The mathematical representation that makes predictions.
Training: Teaching a model using examples.
Overfitting: When a model memorizes rather than generalizes.
Dataset: Collection of labeled or unlabeled data.
Deep Learning: ML technique using neural networks.
Reinforcement Learning: ML type based on reward-driven learning.
Feature: A variable used as input to the model.
15. Frequently Asked Questions
Is machine learning the same as AI?
ML is a subset of AI. AI is broader, ML is specific to learning from data.
Do you need coding to learn ML?
Basic Python helps, but no-code platforms also exist.
Is deep learning better than ML?
Not always. DL is best for large, complex datasets.
Is ML used in LLMs?
Yes — LLMs rely on deep learning, which is a subset of ML.
What industries benefit most from ML?
Finance, healthcare, retail, marketing, manufacturing, tech.
16. Want Daily AI News in Simple Language?
If you enjoy expert guides like this, subscribe to AI Business Weekly — the fastest-growing AI newsletter for business leaders.
👉 Subscribe to AI Business Weekly
https://aibusinessweekly.net




