Last Updated: December 1, 2025
Key Takeaways
Foundation models are large AI models trained on massive, diverse datasets, giving them broad and flexible capabilities.
They power modern AI systems including chatbots, image generators, and multimodal platforms.
Businesses build specialized applications on top of foundation models using fine tuning or retrieval.
Foundation models significantly reduce the cost and time required to develop new AI systems.
They represent a major shift in how organizations build, deploy, and scale AI.
Table of Contents
Overview
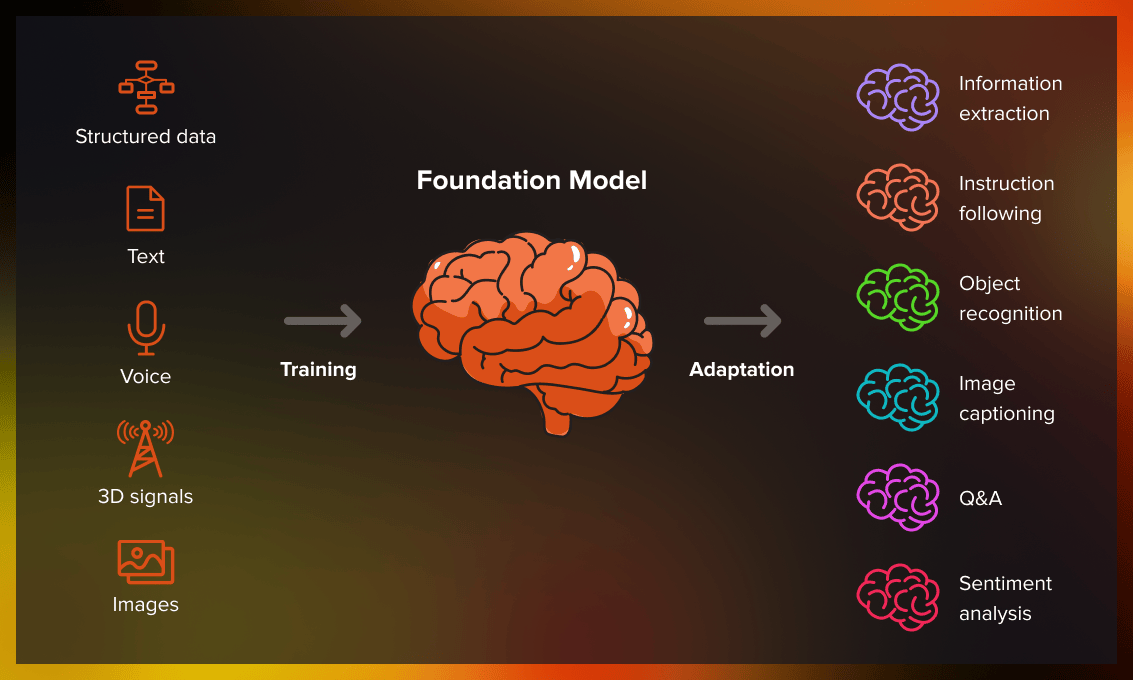
Foundation models are large artificial intelligence models trained on extensive datasets covering a wide range of topics and modalities. They are called foundation models because they act as general purpose platforms that other models and applications can be built on top of.
These models learn broad knowledge about language, images, audio, code, reasoning, and world facts. After training, they can be adapted for specific tasks with far less data and effort than training a model from scratch. This approach has transformed the AI industry because it gives organizations a strong starting point for nearly any application.
Examples of foundation models include GPT, Gemini, Claude, Llama, and many multimodal architectures. They support chat systems, document analysis tools, search engines, recommendation systems, and countless enterprise workflows.
Characteristics of foundation models
Foundation models share several important attributes:
Trained on massive and diverse data
Capable of performing many tasks
Adaptable to new domains with minimal additional training
Scalable across languages and modalities
Serve as platforms for building downstream applications
These characteristics make foundation models one of the most important innovations in modern machine learning.
Foundation models compared to traditional models
Older machine learning systems were task specific. A model for classification could not generate text, and a model for translation could not analyze images. Foundation models broke this pattern by learning broad skills that generalize across many tasks.
Table 1. Traditional Models vs Foundation Models
Category | Traditional Models | Foundation Models |
|---|---|---|
Training data | Narrow and task specific | Massive and diverse |
Capabilities | Single task | Many tasks |
Adaptability | Requires full retraining | Easily fine tuned |
Development cost | High for each task | Lower due to shared base |
Scalability | Limited | Very high |
Example | Sentiment classifier | GPT, Claude, Gemini |
Foundation models unify multiple capabilities into one large system.
How it works
A foundation model is created by training a large neural network on extensive datasets. These datasets often include text, images, audio, video, code, or combinations of these. The goal is not to master one task but to learn general patterns that apply across many tasks.
Training goals
During training, a foundation model learns to:
Understand natural language
Identify concepts in images
Recognize patterns in audio
Predict the next token or output
Learn relationships between modalities
Build a general mental model of how information is structured
These abilities come together to produce flexible and powerful systems.
Why foundation models are useful
Once trained, a foundation model can be adapted to almost any downstream task with minimal extra data. This makes AI development significantly faster and more accessible.
Foundation models also improve performance because they bring vast general knowledge into specialized domains. For example, a foundation model trained on global text sources can understand context, tone, and technical language before it ever sees a company’s internal documents.
Types of foundation models
Foundation models span several categories.
Table 2. Types of Foundation Models
Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Language models | Understand and generate text | GPT, Claude, Llama |
Vision models | Analyze and generate images | DINO, SAM, PixArt |
Multimodal models | Combine text, images, audio, and video | Gemini, GPT 4o |
Code models | Understand and generate programming code | Code Llama, Codex |
Audio models | Process and generate sound | Whisper, AudioGen |
This diversity is one reason foundation models are widely used across industries.
Key points
Why foundation models matter to businesses
Foundation models reduce the complexity of building AI systems. Organizations no longer need to train their own models from scratch. They can take a foundation model and:
Fine tune it on internal data
Add retrieval based systems for knowledge grounding
Integrate it into workflows
Deploy it to serve end users
Customize outputs to match company style and rules
This reduces development time, lowers costs, and improves performance.
Benefits of using foundation models
Key advantages include:
Broad knowledge built into the model
High accuracy and strong generalization
Adaptability through fine tuning or retrieval
Lower barriers to entry for AI adoption
Consistency across tasks and teams
Support for multiple languages and domains
Foundation models give companies a head start that would be impossible with older techniques.
Limitations of foundation models
Foundation models are powerful but not perfect. Limitations include:
High computational requirements
Potential for hallucinations
Difficulty verifying or explaining internal reasoning
Sensitivity to poorly curated fine tuning data
Large memory and storage footprint
These issues drive ongoing research in distillation, efficiency, and reliability.
How companies build on foundation models
Organizations typically combine foundation models with:
Fine tuning
Retrieval augmented generation
System prompts and behavior rules
Guardrails and policy models
Domain specific adapters
These layers turn a general model into a domain expert.
Summary
Foundation models are large AI systems trained on broad and diverse datasets. They serve as the starting point for more specialized models and downstream applications. Because they already understand language, vision, and reasoning patterns, organizations can customize them quickly and cost effectively.
Foundation models are reshaping the AI industry by making advanced capabilities accessible to businesses of all sizes. They combine scalability, generalization, and adaptability in a way previous generations of models could not match.




