Last Updated: November 30th, 2025.
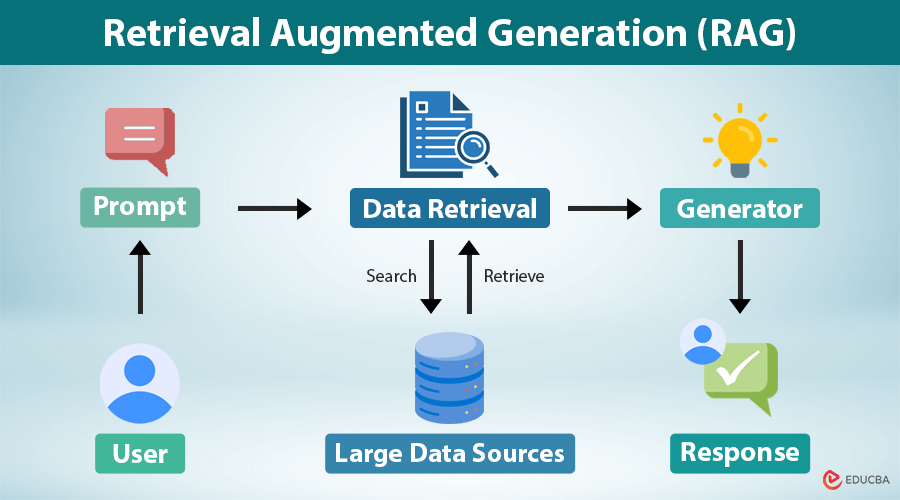
Retrieval-Augmented Generation Diagram
Key Takeaways
RAG stands for Retrieval-Augmented Generation, an AI technique that combines search retrieval with generative models.
It improves accuracy by grounding AI responses in real documents instead of relying only on what the model was trained on.
RAG reduces hallucinations, boosts reliability, and is widely used in chatbots, enterprise AI tools, and search systems.
Companies use RAG to integrate their own data into AI systems without retraining large models.
RAG is becoming a core part of modern AI applications due to its flexibility and trustworthiness.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding the Meaning of RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation, or RAG, is an AI approach that combines two components:
Retrieval: Searching through a database or knowledge source to pull up relevant documents.
Generation: Using an AI model (like GPT or Claude) to turn those documents into a clear response.
The core idea is simple.
Instead of letting an AI model answer a question based only on what it learned during training, you first retrieve real, up-to-date information and then generate an answer based on that information.
This approach makes the final output more accurate and grounded in facts.
In today’s AI landscape, RAG is one of the most important techniques because businesses want AI systems that reliably use their own data — not just general internet knowledge.
2. Why RAG Exists and What Problem It Solves
Large language models (LLMs) are powerful, but they have two major limitations:
1. They do not automatically know your private data.
An LLM can’t access your company files, PDFs, or databases unless it’s given that information.
2. They sometimes hallucinate.
This means they produce answers that sound correct but are factually wrong.
RAG solves both problems at once.
With RAG, the AI model retrieves relevant documents from a trusted source and uses them to generate a grounded, evidence-based answer.
The model is no longer “guessing” based strictly on training. It is referencing.
This drastically reduces hallucinations.
3. How RAG Works Step-by-Step
A typical RAG pipeline works like this:
Step 1: Ingest Data
Documents are added to a database. These can include:
PDFs
emails
websites
product manuals
API documentation
internal reports
help desk tickets
Step 2: Chunk and Index
Long documents are broken into smaller chunks and stored in a vector database like Pinecone, Weaviate, Milvus, or Chroma.
Step 3: Embed the Text
Each chunk of text is converted into a vector, a numerical representation of meaning.
Step 4: Retrieve Relevant Chunks
When a user asks a question, the system retrieves the most relevant document chunks based on meaning, not keyword matching.
Step 5: Generate an Answer
The retrieved chunks are given to an LLM, which uses them to produce a grounded, contextual response.
Step 6: Return the Final Output
The system returns the answer with sources, citations, or linked documents.
This process happens in milliseconds.
4. Real Examples of RAG in Action
Here are some common ways RAG is used today.
Customer Support Chatbots
A RAG chatbot can search through your knowledge base and customer support history to give accurate answers based on real documentation.
Internal Company Assistants
Companies build AI assistants that pull from:
Confluence
Google Drive
SharePoint
Notion
Slack
Internal databases
This lets employees access information instantly.
Search Engines and Research Tools
Modern search tools use RAG to pull relevant sources and then summarize them clearly.
Developer Assistants
AI coding tools retrieve documentation, APIs, and examples to answer technical questions accurately.
Healthcare & Legal Systems
Professionals use RAG to search through medical research, case law, or regulations before answering.
RAG is everywhere because it provides something LLMs alone cannot:
trustworthy, cited answers.
5. Why RAG Beats Traditional AI for Enterprise Use
Businesses rely heavily on RAG for several reasons:
1. Uses your actual company data
The model answers questions based on your specific documents, not general internet text.
2. No need to retrain huge models
RAG avoids the cost of fine-tuning massive LLMs with proprietary data.
3. Reduces hallucinations
Because answers come from retrieved documents, accuracy improves dramatically.
4. Low cost and easy to maintain
Updating the database is much cheaper than retraining an LLM.
5. Perfect for confidential environments
You can keep documents private while still leveraging LLMs.
This is why companies building AI assistants almost always start with a RAG system.
6. Strengths and Limitations of RAG Systems
Strengths
High accuracy
Uses real documents
Transparent sources
Tailored to the organization
Easy to update
Significantly reduces hallucinations
Limitations
Retrieval quality matters
Bad chunking leads to bad answers
Complex documents require careful preprocessing
Does not fully eliminate hallucinations
Might struggle with abstract reasoning that goes beyond retrieved context
RAG is powerful, but it is not magic.
It works best when the documents are high-quality and well-structured.
7. RAG vs Fine-Tuning: Key Differences
RAG and fine-tuning are often confused, but they serve different purposes.
Feature | RAG | Fine-Tuning |
|---|---|---|
Input | Uses external documents | Changes model weights |
Cost | Low | High |
Speed | Fast | Slow |
Control | Very specific | Broadly improved behavior |
Best For | Factual accuracy | New model skills |
Best rule of thumb:
If you want accuracy, use RAG.
If you want new abilities, use fine-tuning.
Together, they can be extremely powerful.
8. Industries Using RAG Today
RAG has become a core part of AI adoption across industries:
Healthcare: medical literature retrieval
Legal: case law, regulations, contracts
Finance: compliance, risk, reporting
Education: personalized learning and research
Technology: software documentation and developer support
E-commerce: product search, real-time recommendations
Customer Service: knowledge base retrieval
Government: policy lookup and internal research
Anywhere information must be accurate and sourced, RAG is a good fit.
9. Glossary
RAG: Retrieval-Augmented Generation, combining search retrieval with AI generation.
Vector Database: Database designed to store embeddings.
Embedding: A numerical representation of text meaning.
Chunking: Splitting documents into smaller pieces.
Hallucination: When AI produces factually incorrect answers.
10. Frequently Asked Questions
Does RAG remove hallucinations completely?
No, but it significantly reduces them.
Is RAG better than fine-tuning?
For accuracy and sourcing, yes. For teaching new skills, no.
Does RAG work with any LLM?
Yes, including GPT, Claude, Gemini, and LLaMA models.
Is RAG expensive?
Generally no. It is more cost-efficient than training models.
Can small companies use RAG?
Absolutely. Even small teams can build RAG systems with open-source tools.
11. Want Daily AI News in Plain Language?
Join AI Business Weekly for concise, clear updates on AI, AGI, funding news, and major breakthroughs.





